Understanding Venous Stasis Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
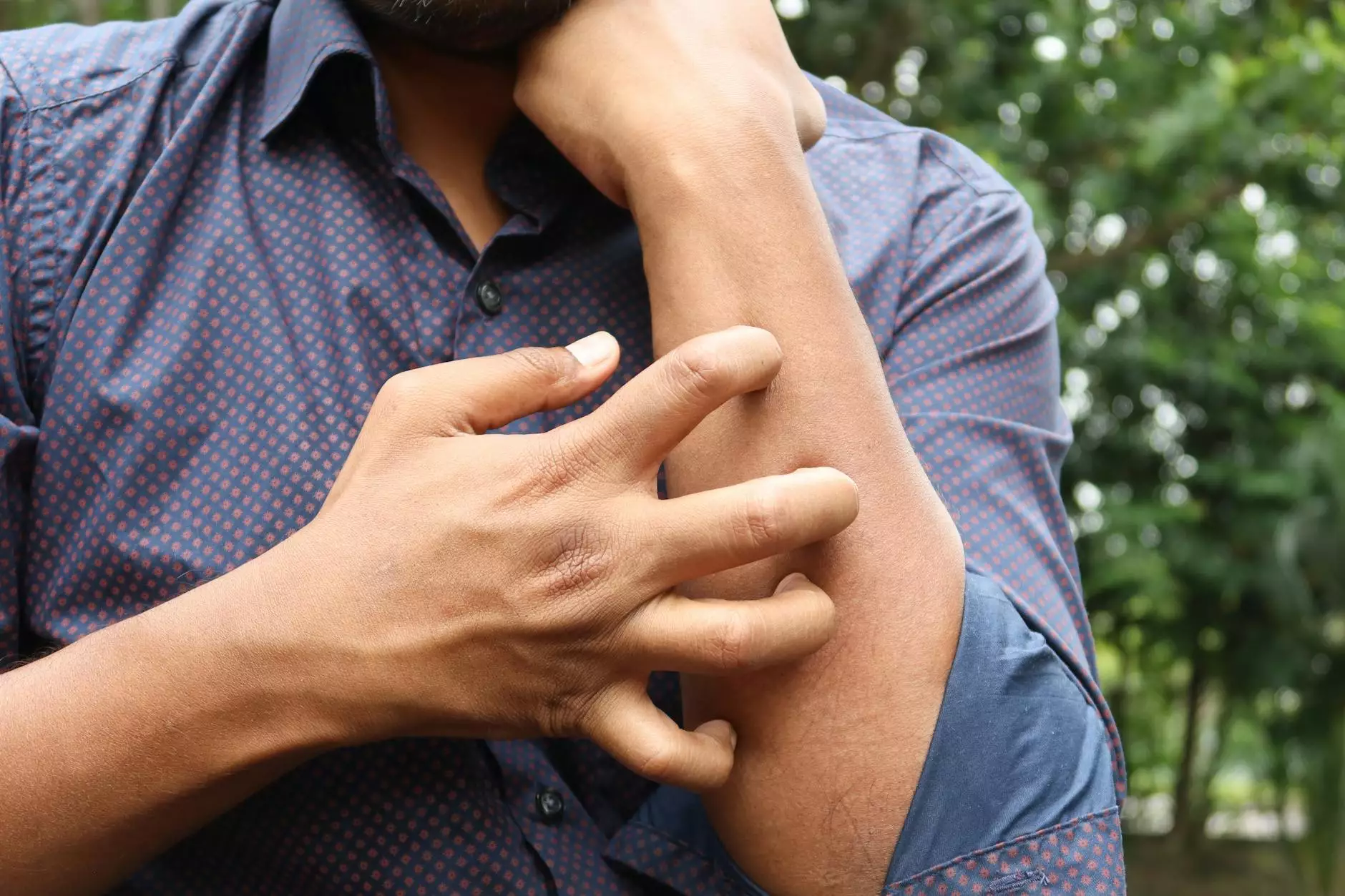

Venous stasis dermatitis is a common skin condition that arises due to poor circulation and prolonged venous hypertension, typically found in the legs. It can lead to significant discomfort and has various implications for those affected. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventative measures associated with this condition, allowing you to stay informed and proactive about your vascular health.
What is Venous Stasis Dermatitis?
Venous stasis dermatitis is characterized by inflammation of the skin, particularly in the lower extremities, as a result of venous insufficiency. This condition occurs when veins in the legs struggle to send blood back to the heart, causing blood to pool in the veins. This pooling can lead to a range of symptoms, including swelling, discoloration, and itching.
Causes of Venous Stasis Dermatitis
Understanding the underlying causes of venous stasis dermatitis is crucial for effective management and prevention. The primary causes include:
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI): This is the most common cause. It happens when the valves in the veins of the legs fail to function correctly, leading to blood pooling.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins, worsening circulation and increasing the risk of CVI.
- Age: As individuals age, venous wall elasticity decreases, often resulting in venous insufficiency.
- Previous Blood Clots: A history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can damage the valves in the veins, leading to chronic issues.
- Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Occupations or lifestyles that involve long periods without movement can negatively affect circulation.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased blood volume during pregnancy can contribute to venous insufficiency.
Symptoms of Venous Stasis Dermatitis
The symptoms of venous stasis dermatitis can vary in intensity, but they typically include:
- Swelling in the lower legs and ankles.
- Itching or irritation of the skin.
- Redness or discoloration, particularly around the ankles.
- Dry or flaky skin that may develop crusting or scaling.
- Thickening of the skin or changes in texture.
- Open sores or ulcers in severe cases.
Diagnosis of Venous Stasis Dermatitis
Diagnosing venous stasis dermatitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests. During a consultation, a healthcare provider will:
- Review your medical history, focusing on any symptoms and risk factors.
- Conduct a physical examination of the affected areas.
- Utilize imaging techniques such as duplex ultrasound to assess blood flow and identify any underlying venous insufficiency.
Treatments for Venous Stasis Dermatitis
Effective management of venous stasis dermatitis requires a comprehensive treatment approach, often involving multiple strategies:
1. Lifestyle Changes
Implementing lifestyle changes can be key to managing symptoms and reducing the risk of complications:
- Regular Exercise: Activity such as walking can improve circulation.
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight can relieve pressure on the veins.
- Elevation of the Legs: Keeping your legs elevated can help reduce swelling.
2. Compression Therapy
Compression stockings are often prescribed to help support vein function and improve blood flow. These garments apply pressure to the legs, encouraging blood to return to the heart and reducing swelling.
3. Topical Treatments
Using medicated creams and ointments can assist in managing inflammation and irritation:
- Hydrocortisone Cream: A mild steroid that can alleviate inflammation.
- Moisturizers: Keeping the skin hydrated can prevent further flare-ups.
4. Medications
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medications to manage symptoms or address underlying conditions:
- Oral Antihistamines: For itching and allergic reactions.
- Antibiotics: If an infection develops from open sores.
5. Surgical Options
In severe or resistant cases of venous stasis dermatitis, surgical procedures may be considered:
- Vein Stripping: Removing damaged veins to improve blood flow.
- Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT): A minimally invasive procedure to close off problematic veins.
Preventive Measures for Venous Stasis Dermatitis
Prevention plays a vital role in managing venous stasis dermatitis and reducing the risk of complications. Effective measures include:
- Staying Active: Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine.
- Avoiding Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Take breaks to walk around, especially during long periods of inactivity.
- Wearing Compression Stockings: Especially during long travels or sitting tasks.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Regular exercise and a balanced diet help manage weight effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding venous stasis dermatitis is essential for individuals affected by this condition. Being aware of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers you to take control of your vascular health. By implementing a proactive approach involving lifestyle changes, appropriate medical treatments, and preventive measures, you can significantly improve your quality of life. If you suspect you have venous stasis dermatitis, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
For more information on managing venous conditions, feel free to visit Truffles Vein Specialists, where our dedicated team of experts in vascular medicine is committed to providing the highest standard of care.